In honour of World Tuberculosis Day, we have a guest blog from Rebecca Cessford. Rebecca is a PhD researcher with the AHRC funded Heritage Consortium based at the Universities of Hull and Bradford. She will be using the Stannington Sanatorium Collection to study tuberculosis in the past using the archaeology of human remains and medical history. Here she tells us about her research and the role of the Stannington Collection in it.
When we think of tuberculosis (TB), images are conjured of a romantic disease causing a bloody cough, a pale complexion and weight-loss, the romanticised disease of the 19th century. What we do not think of is TB roaming the streets today. But tuberculosis is still a great threat, with over a million people dying of the disease each year and over 6,500 new cases declared in the UK during 2014. With increasing multidrug resistant strains of tuberculosis, is it possible to look back at a time before antibiotic drug therapy to better understand the future of this global emergency?

Tuberculosis is a disease that extends as far back as the Neolithic period in Europe, with the earliest case reported in England coming from Dorset dating to the Iron Age. However, our ability to identify tuberculosis in skeletal remains from archaeological contexts is difficult. Firstly, tuberculosis of the bones and joints only affects 3-5% of all cases. Secondly, bone can only react to disease in a limited number of ways with many diseases causing similar bony destruction and remodelling. There are also problems identifying tuberculosis in the remains of children, due mainly to the under-representation of children in the archaeological record.
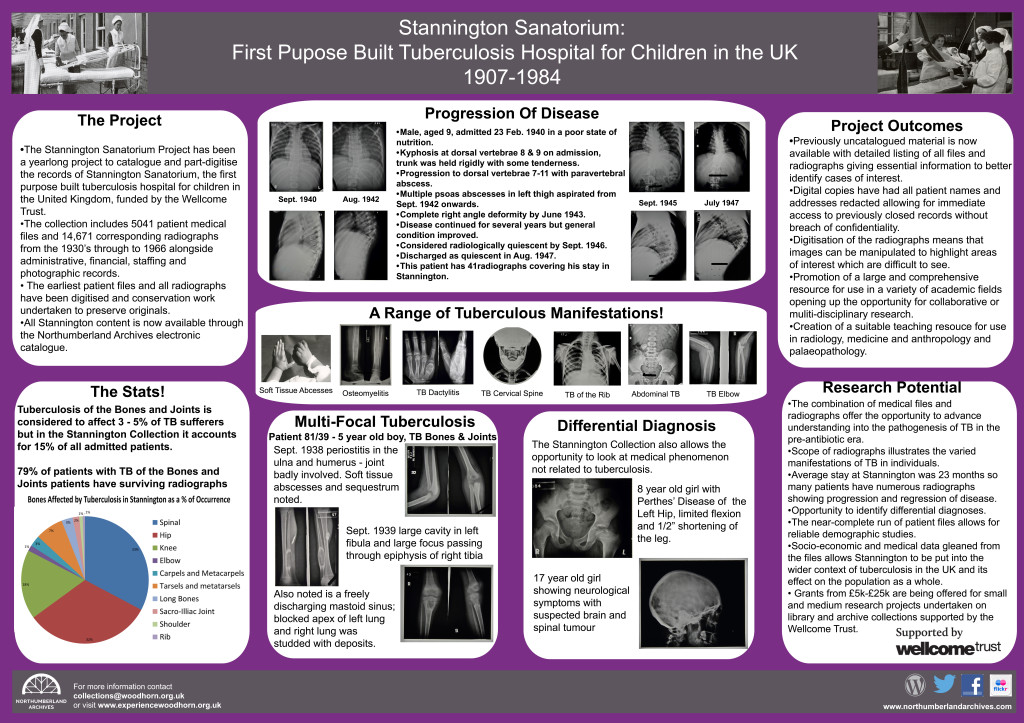
The most characteristic feature of tuberculosis in the skeleton is Pott’s Spine, an angular deformity in the mid to lower spinal column caused by the collapse of one or more vertebral bodies. The presence of this deformity has, for many years, been the only way of diagnosing tuberculosis in human remains with any certainty, despite the fact that any bone in the body can be affected. Advances in ancient DNA and biomolecular studies in archaeology mean tuberculosis can be tested for, even in the absence of any physical pathologies. However, these destructive and costly procedures are not without their limitations, still leaving much reliance on routine macroscopic observations (seen with the naked eye) of dry bone remains.
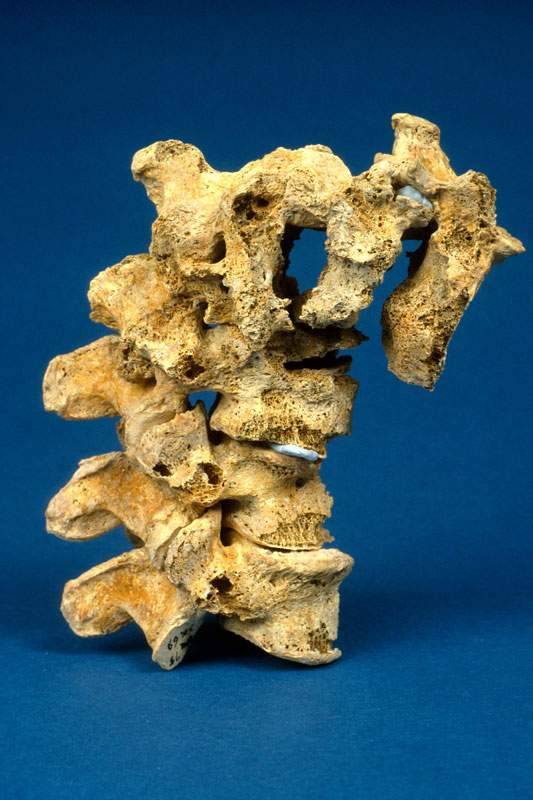

My research aims to look at the potential for using pre-antibiotic clinical radiographs (x- rays) as an aid to the macroscopic identification of tuberculosis in human remains, focussing specifically on infants and children. To do this, I intend to undertake a thorough examination of all the radiographs demonstrating skeletal tuberculosis to look at variations in progression of disease over time; the outcomes of healing on bones and the distribution of tuberculosis across the body where more than one bone was involved. In addition to this I will look at the corresponding medical file for each set of radiographs drawing on details outlined in the medical notes and x-ray reports to add to my own observations from the radiographs for an informed review of the underlying processes to bone and soft tissue being observed. It is hoped that the compilation of this data will provide a more detailed understanding of the processes involved in advancing tuberculous infection with comparative examples from pre-antibiotic radiographs. This strives to increase the ability to diagnose tuberculosis in archaeological remains even in the absence of Pott’s Spine.
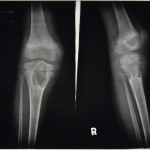
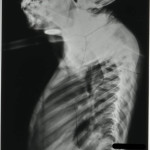
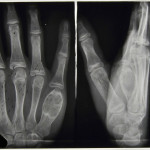
By studying the patterns of tuberculosis in the past we are better informed when it comes to dealing with the disease in the present and in the future. To be able to offer an evidence-based and informed approach to tackling tuberculosis we need better criteria for diagnosing it macroscopically in archaeological human remains, to get a more encompassing view of the various manifestations associated with it. The outcomes of my research will aim to act as an aid to the identification and study of tuberculosis in children in relation to archaeological remains further identifying the worth of pre-antibiotic medical records.
The Stannington Collection is a unique resource for studying this long standing infectious disease in children from the early to mid-20th century, many of which are still alive today living with the memories and/or side effects of the disease. I would also like to take this opportunity to thank the former patients of Stannington Sanatorium who expressed support for academic research to be undertaken on the collection during the first phase of the Stannington Sanatorium Project; their support makes research all the more worthwhile.